17
янв
Freenas Virtio Drivers
Posted:adminThat process was a bit daunting because the OmniOS installer doesn’t include the virtio drivers by default, so I had to install to an IDE disk, pull in the virtio drivers from the pkg repos, attach a virtio disk, add the new drive to the root pool, then remove the old one.  For debian the LACP is working properly. (network virtIO bonding on vm) For freeNAS the LACP does not work. (network virtIO lagg on vm) Physical machine Same test with a physical machine (same hardware/switch) FreeNAS work on LACP As a result I deduced the virtIO function on FreeNAS (11.1U6) does not work for the LACP (802.3ad).
For debian the LACP is working properly. (network virtIO bonding on vm) For freeNAS the LACP does not work. (network virtIO lagg on vm) Physical machine Same test with a physical machine (same hardware/switch) FreeNAS work on LACP As a result I deduced the virtIO function on FreeNAS (11.1U6) does not work for the LACP (802.3ad).
If you plan on running Windows, it is highly advised that you are running FreeBSD 11+ and use UEFI graphics support. First of all you will need to make sure you have the UEFI firmware if not already installed: # pkg install bhyve-firmware Guest Configuration Create a guest using the Windows template. This guest defaults to 2 cpus and 2GB of memory. It also uses an e1000 Intel network adapter which is support by Windows out-of-the-box. Use the vm configure guest command if you would like to change also configuration options. Note that if you are running a version of Windows older than Windows 10, you will need to set the disk sector size to 512 using the disk0_opts='sectorsize=512' option.
# vm create -t windows winguest Installation Start the installation as normal by specifying the Windows iso file. When run in install mode, vm-bhyve will wait until a VNC client is connected before starting the guest. This allows you to catch the 'Boot from CD/DVD' option that Windows may display. You can see in vm list that the guest will show as locked at this point.
# vm install winguest Windows-Installer.iso Once connected with a VNC client, complete the Windows installation as normal. Adding VirtIO network drivers While the e1000 network adapter works out of the box and allows the guest to get network access, it is recommended to use the virtio-net device where possible. There are several ways of installing these drivers. • If the machine has Internet access via the e1000 device, you can download and install the virtio drivers directly in the guest. Once installed, shutdown the guest, change the device in guest configuration and restart.
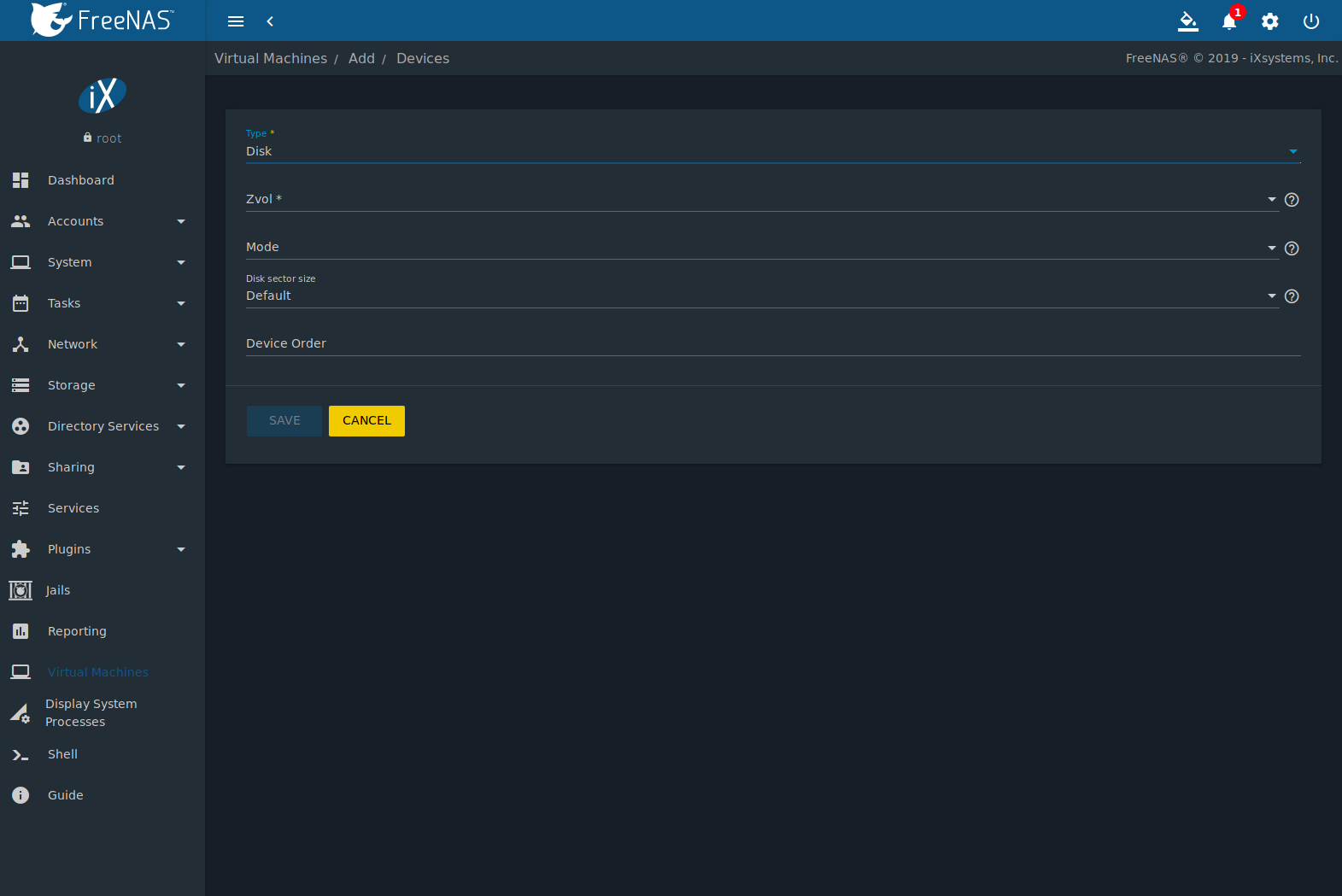
• The guest can be booted in install mode, but specifying the VirtIO ISO file. # vm install winguest virtio-installer.iso • A CD device can be added to the guest and pointed at the ISO file disk1_type='ahci-cd' disk1_dev='custom' disk1_name='/full/path/to/virtio-installer.iso' Regarding CPUs Some versions of Windows (most desktop versions) do not support more than one physical CPU. By default, bhyve configures every virtual CPU and a separate package.
The hw.vmm.topology.cores_per_package sysctl can be modified to tell bhyve to create multiple cores per CPU, rather than separate packages. For example, setting this sysctl to 4 will cause a guest with 8 vCPUs to have 2 x 4 core packages. Hw.vmm.topology.cores_per_package must be set in /boot/loader.conf (and a reboot to take effect). On FreeBSD 12, when using vm-bhyve 1.3, it's possible to control CPU topology for each guest using configuration options - cpu=8 cpu_sockets=2 cpu_cores=4 cpu_threads=1.
Virtio on FreeBSD virtio binary packages for FreeBSD KVM and VirtualBox (and BHyVe?) support virtio, and we finally have virtio drivers in base tree. These virtualization technologies are sometimes used in resource restricted VPS and IaaS environments.
' Wifi HotSpot' can easily turn your windows pc into a wireless-wifi hotspot. Tutorial jaringan wifi. With one click you can share your internet connection with your mobile phone, iPhone, iPad, tablet, computer or any other wireless enabled devices. It turns your Windows 7, Windows 8 or Windows 10 computer into a virtual router. Wifi HotSpot is the perfect solution for sharing your internet connection when you don't have a wireless router or if your using a mobile internet connected service such as Verizon, Sprint, Clear Wireless etc.
For those environments, I made pre-built binary packages of virtio kernel loadble modules. You can activate virtio devices in your FreeBSD guests with only pkg_add, edit rc.conf/fstab, change host setting, and rebooting.
Binary Packages Currenly amd64 arch only. Releases Packages 9.1-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) 9.0-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (2012-04-22) (2012-01-09) 8.4-RELEASE (2013-06-11) 8.3-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (2012-04-22) 8.2-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (r234349 cannot be compiled on 8.2) (2012-01-09) (2011-11-22).
Popular Posts
That process was a bit daunting because the OmniOS installer doesn’t include the virtio drivers by default, so I had to install to an IDE disk, pull in the virtio drivers from the pkg repos, attach a virtio disk, add the new drive to the root pool, then remove the old one.
 For debian the LACP is working properly. (network virtIO bonding on vm) For freeNAS the LACP does not work. (network virtIO lagg on vm) Physical machine Same test with a physical machine (same hardware/switch) FreeNAS work on LACP As a result I deduced the virtIO function on FreeNAS (11.1U6) does not work for the LACP (802.3ad).
For debian the LACP is working properly. (network virtIO bonding on vm) For freeNAS the LACP does not work. (network virtIO lagg on vm) Physical machine Same test with a physical machine (same hardware/switch) FreeNAS work on LACP As a result I deduced the virtIO function on FreeNAS (11.1U6) does not work for the LACP (802.3ad).If you plan on running Windows, it is highly advised that you are running FreeBSD 11+ and use UEFI graphics support. First of all you will need to make sure you have the UEFI firmware if not already installed: # pkg install bhyve-firmware Guest Configuration Create a guest using the Windows template. This guest defaults to 2 cpus and 2GB of memory. It also uses an e1000 Intel network adapter which is support by Windows out-of-the-box. Use the vm configure guest command if you would like to change also configuration options. Note that if you are running a version of Windows older than Windows 10, you will need to set the disk sector size to 512 using the disk0_opts=\'sectorsize=512\' option.
# vm create -t windows winguest Installation Start the installation as normal by specifying the Windows iso file. When run in install mode, vm-bhyve will wait until a VNC client is connected before starting the guest. This allows you to catch the \'Boot from CD/DVD\' option that Windows may display. You can see in vm list that the guest will show as locked at this point.
# vm install winguest Windows-Installer.iso Once connected with a VNC client, complete the Windows installation as normal. Adding VirtIO network drivers While the e1000 network adapter works out of the box and allows the guest to get network access, it is recommended to use the virtio-net device where possible. There are several ways of installing these drivers. • If the machine has Internet access via the e1000 device, you can download and install the virtio drivers directly in the guest. Once installed, shutdown the guest, change the device in guest configuration and restart.

• The guest can be booted in install mode, but specifying the VirtIO ISO file. # vm install winguest virtio-installer.iso • A CD device can be added to the guest and pointed at the ISO file disk1_type=\'ahci-cd\' disk1_dev=\'custom\' disk1_name=\'/full/path/to/virtio-installer.iso\' Regarding CPUs Some versions of Windows (most desktop versions) do not support more than one physical CPU. By default, bhyve configures every virtual CPU and a separate package.
The hw.vmm.topology.cores_per_package sysctl can be modified to tell bhyve to create multiple cores per CPU, rather than separate packages. For example, setting this sysctl to 4 will cause a guest with 8 vCPUs to have 2 x 4 core packages. Hw.vmm.topology.cores_per_package must be set in /boot/loader.conf (and a reboot to take effect). On FreeBSD 12, when using vm-bhyve 1.3, it\'s possible to control CPU topology for each guest using configuration options - cpu=8 cpu_sockets=2 cpu_cores=4 cpu_threads=1.
Virtio on FreeBSD virtio binary packages for FreeBSD KVM and VirtualBox (and BHyVe?) support virtio, and we finally have virtio drivers in base tree. These virtualization technologies are sometimes used in resource restricted VPS and IaaS environments.
\' Wifi HotSpot\' can easily turn your windows pc into a wireless-wifi hotspot. Tutorial jaringan wifi. With one click you can share your internet connection with your mobile phone, iPhone, iPad, tablet, computer or any other wireless enabled devices. It turns your Windows 7, Windows 8 or Windows 10 computer into a virtual router. Wifi HotSpot is the perfect solution for sharing your internet connection when you don\'t have a wireless router or if your using a mobile internet connected service such as Verizon, Sprint, Clear Wireless etc.
For those environments, I made pre-built binary packages of virtio kernel loadble modules. You can activate virtio devices in your FreeBSD guests with only pkg_add, edit rc.conf/fstab, change host setting, and rebooting.
Binary Packages Currenly amd64 arch only. Releases Packages 9.1-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) 9.0-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (2012-04-22) (2012-01-09) 8.4-RELEASE (2013-06-11) 8.3-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (2012-04-22) 8.2-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (r234349 cannot be compiled on 8.2) (2012-01-09) (2011-11-22).
...'>Freenas Virtio Drivers(17.01.2019)That process was a bit daunting because the OmniOS installer doesn’t include the virtio drivers by default, so I had to install to an IDE disk, pull in the virtio drivers from the pkg repos, attach a virtio disk, add the new drive to the root pool, then remove the old one.
 For debian the LACP is working properly. (network virtIO bonding on vm) For freeNAS the LACP does not work. (network virtIO lagg on vm) Physical machine Same test with a physical machine (same hardware/switch) FreeNAS work on LACP As a result I deduced the virtIO function on FreeNAS (11.1U6) does not work for the LACP (802.3ad).
For debian the LACP is working properly. (network virtIO bonding on vm) For freeNAS the LACP does not work. (network virtIO lagg on vm) Physical machine Same test with a physical machine (same hardware/switch) FreeNAS work on LACP As a result I deduced the virtIO function on FreeNAS (11.1U6) does not work for the LACP (802.3ad).If you plan on running Windows, it is highly advised that you are running FreeBSD 11+ and use UEFI graphics support. First of all you will need to make sure you have the UEFI firmware if not already installed: # pkg install bhyve-firmware Guest Configuration Create a guest using the Windows template. This guest defaults to 2 cpus and 2GB of memory. It also uses an e1000 Intel network adapter which is support by Windows out-of-the-box. Use the vm configure guest command if you would like to change also configuration options. Note that if you are running a version of Windows older than Windows 10, you will need to set the disk sector size to 512 using the disk0_opts=\'sectorsize=512\' option.
# vm create -t windows winguest Installation Start the installation as normal by specifying the Windows iso file. When run in install mode, vm-bhyve will wait until a VNC client is connected before starting the guest. This allows you to catch the \'Boot from CD/DVD\' option that Windows may display. You can see in vm list that the guest will show as locked at this point.
# vm install winguest Windows-Installer.iso Once connected with a VNC client, complete the Windows installation as normal. Adding VirtIO network drivers While the e1000 network adapter works out of the box and allows the guest to get network access, it is recommended to use the virtio-net device where possible. There are several ways of installing these drivers. • If the machine has Internet access via the e1000 device, you can download and install the virtio drivers directly in the guest. Once installed, shutdown the guest, change the device in guest configuration and restart.

• The guest can be booted in install mode, but specifying the VirtIO ISO file. # vm install winguest virtio-installer.iso • A CD device can be added to the guest and pointed at the ISO file disk1_type=\'ahci-cd\' disk1_dev=\'custom\' disk1_name=\'/full/path/to/virtio-installer.iso\' Regarding CPUs Some versions of Windows (most desktop versions) do not support more than one physical CPU. By default, bhyve configures every virtual CPU and a separate package.
The hw.vmm.topology.cores_per_package sysctl can be modified to tell bhyve to create multiple cores per CPU, rather than separate packages. For example, setting this sysctl to 4 will cause a guest with 8 vCPUs to have 2 x 4 core packages. Hw.vmm.topology.cores_per_package must be set in /boot/loader.conf (and a reboot to take effect). On FreeBSD 12, when using vm-bhyve 1.3, it\'s possible to control CPU topology for each guest using configuration options - cpu=8 cpu_sockets=2 cpu_cores=4 cpu_threads=1.
Virtio on FreeBSD virtio binary packages for FreeBSD KVM and VirtualBox (and BHyVe?) support virtio, and we finally have virtio drivers in base tree. These virtualization technologies are sometimes used in resource restricted VPS and IaaS environments.
\' Wifi HotSpot\' can easily turn your windows pc into a wireless-wifi hotspot. Tutorial jaringan wifi. With one click you can share your internet connection with your mobile phone, iPhone, iPad, tablet, computer or any other wireless enabled devices. It turns your Windows 7, Windows 8 or Windows 10 computer into a virtual router. Wifi HotSpot is the perfect solution for sharing your internet connection when you don\'t have a wireless router or if your using a mobile internet connected service such as Verizon, Sprint, Clear Wireless etc.
For those environments, I made pre-built binary packages of virtio kernel loadble modules. You can activate virtio devices in your FreeBSD guests with only pkg_add, edit rc.conf/fstab, change host setting, and rebooting.
Binary Packages Currenly amd64 arch only. Releases Packages 9.1-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) 9.0-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (2012-04-22) (2012-01-09) 8.4-RELEASE (2013-06-11) 8.3-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (2012-04-22) 8.2-RELEASE (2013-06-11) (2012-11-06) (2012-08-23) (r234349 cannot be compiled on 8.2) (2012-01-09) (2011-11-22).
...'>Freenas Virtio Drivers(17.01.2019)